Back in 2012, German software developer, maker, and excellent tour guide, Gina Häußge, got her first 3D printer . She subsequently wrote and released a free, open source 3D printer host controller application called OctoPrint which allows users to remotely control and monitor prints from a web browser.
“That’s nice,” you might say, “but what makes OctoPrint any different from all the other 3D printer host apps out there?” The thing that sets OctoPrint apart is its extremely versatile, pluggable framework.

The framework Häußge designed has attracted a community of developers who, in turn, continually extend OctoPrint’s features and functionality through plugins. There are currently 277 plugins in OctoPrint’s repository. Häußge says, “All in all 194 plugin authors have spent time and effort to bring you these plugins.”
Below, we’ll take a look at some of the best tools and toys for OctoPrint—plugins that will help you create better prints as well as a few that are just for fun. All these plugins can be installed for free via the OctoPrint interface.
Tools: Best Octoprint Plugins for Better Prints
Predictably, most plugins for OctoPrint are tools to help you make better prints . Installing and using the plugins below will help you improve your 3D printing game.
1.Bed Level Visualizer
To get good prints on your 3D printer, the first thing you need to do is make sure your printer’s bed is level. It’s a difficult, time-consuming process that uses up a lot of filament and can be very frustrating.
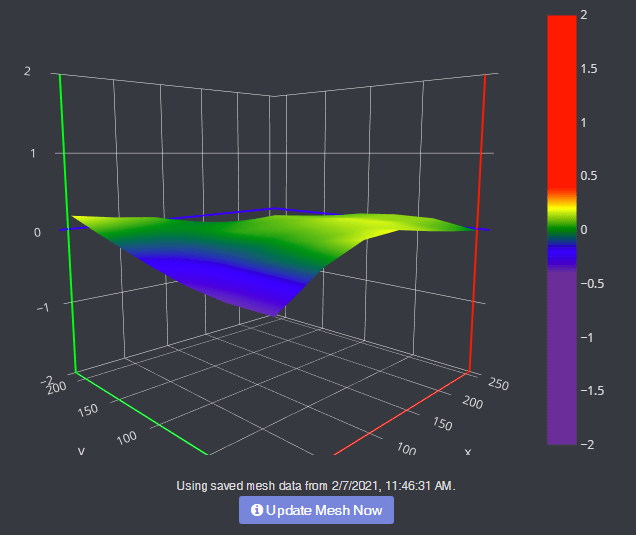
Bed Level Visualizer takes the guesswork out of that process by showing you a topographical map of your bed so you know which areas are high and which are low. If you want your bed to be perfectly level (hint: you do), this is the first OctoPrint plugin you should install. It requires that you have an auto-bed-leveling tool like BLTouch .
2.Enclosure
Putting your 3D printer inside an enclosure helps you control the printer’s environment, which leads to better quality prints. If you have an enclosure, install this plugin, and you’ll be able to control lights, switches, power, or any other sensor you can plug into your Raspberry Pi .
You can view temp sensors, filament run-out sensors, turn your LED lights on and off, or even change the color of your LED lights. This plugin is super-flexible and can control almost any aspect of your enclosure environment that you can imagine.
3. The Spaghetti Detective
When a print goes wrong, the result can look like a plateful of spaghetti. Moreover, if you’ve left your printer unattended, you won’t even know your print has failed until you check.
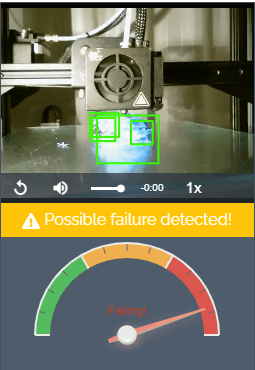
Enter The Spaghetti Detective, an OctoPrint plugin that puts AI deep learning to use by analyzing the images from your webcam for any indication that your print is failing. In other words, The Spaghetti Detective will detect failed prints and send you a message so you can react accordingly.
4.Pretty GCode
The Pretty GCode plugin is an excellent 3D model viewer. Click on your GCode file and watch it render before your eyes. Rotate, zoom in on, and detect problems with your GCode files before you print. Pretty GCode even renders arc commands.
5.Firmware Updater
All software should be updated regularly. Updating your printer’s firmware can be a pain, requiring you to download the update to an SD card and then installing it locally on your printer.
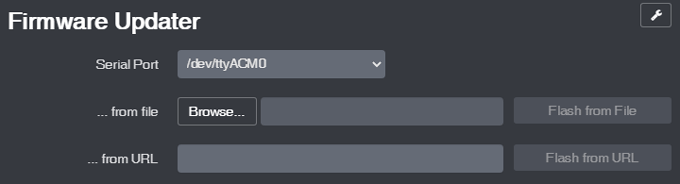
The Firmware Updater plugin allows you to flash your printer’s firmware from within OctoPrint. Just drop in the update file or URL, click a button, and soon your printer will be running the latest firmware.
6.Arc Welder*
Faulty power supplies, bad USB cables, slow serial connections, and slicer problems can all conspire to overwhelm your printer with GCode. If too many commands are sent or if your connection is slowed down, that can cause your printer to stall, and you’ll probably see evidence of every stall on your printed part. Entire forums are dedicated to solving this problem, and a lot of the advice involves recompiling firmware or other difficult operations that may or may not solve the problem.
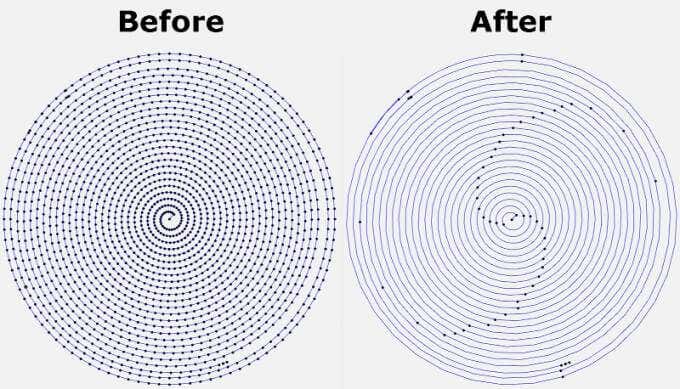
The Arc Welder plugin is perhaps the simplest fix. It reduces the number of GCodes sent to your printer— sometimes dramatically—by compressing some GCodes into arc commands. In many cases, installing Arc Welder will completely eliminate stuttering and stalling and improve your print times and quality. Not all firmware supports arc commands, but if yours does, this should be on your must-install list.
Toys: Best Octoprint Plugins for Fun
The plugins above will help you improve the quality of your 3D prints. The plugins listed below will help improve how you interact with OctoPrint and increase how much fun you have.
7.Octolapse*
Have you seen the videos ? A beautiful 3D print arises from the printer bed like magic. It’s not magic, though. It’s Octolapse. This OctoPrint plugin creates stabilized timelapse videos of your 3D prints. It does this by moving your printer’s extruder out of the way and your printer bed into optimal position before it takes each snapshot so you end up with a really smooth timelapse.
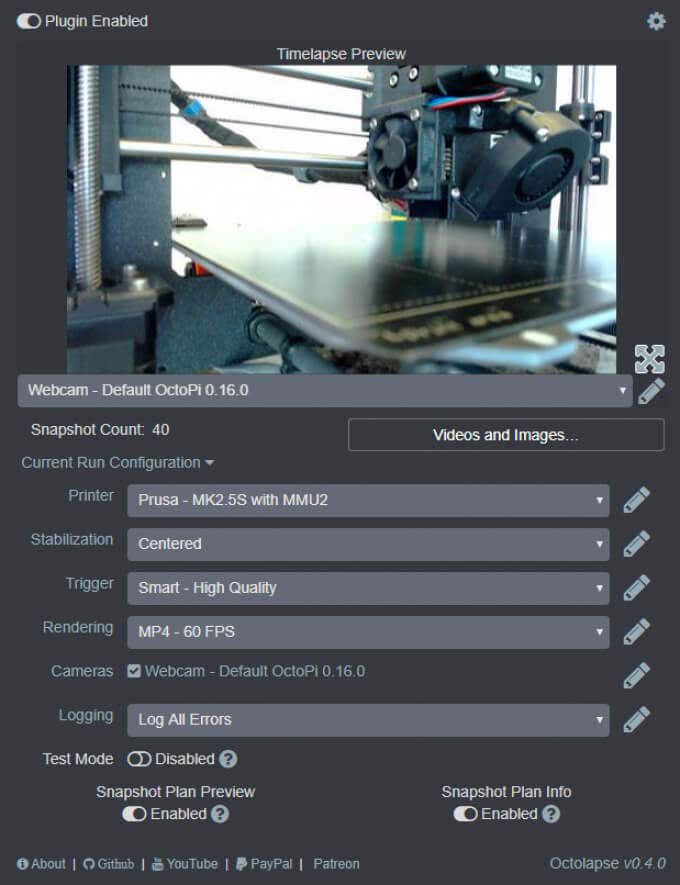
Put another way, you won’t see your printhead moving around in the timelapse, just your print growing from the printer bed. You can set specific triggers for snapshots such as at each layer change, at preset time or height increments, or when particular GCodes are sent to your printer.
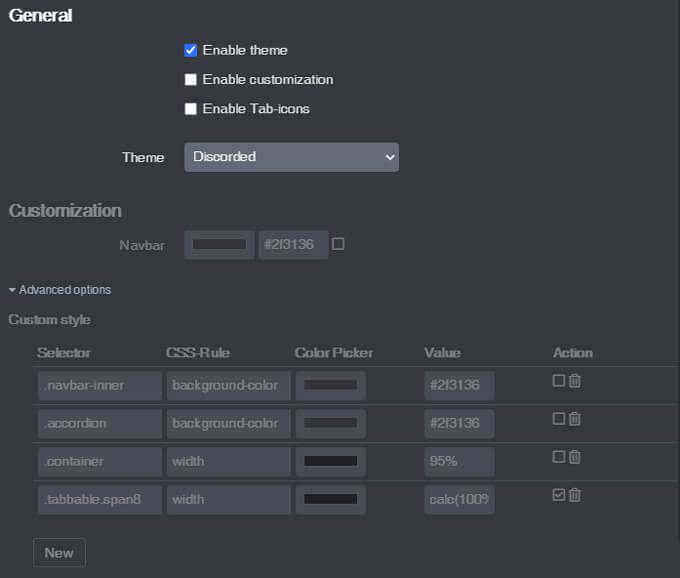
8.Themeify
Given the option, many people will choose a dark theme for the apps and web pages they use most. The Themeify plugin allows you to apply themes to OctoPrint. Choose dark mode or from a variety of other pre-set themes. If you know CSS, you can customize virtually any element of the OctoPrint interface.
9.Fullscreen Webcam
Are you tired of watching your webcam in OctoPrint’s tiny control window? Maximize it with the Fullscreen Webcam plugin. It does exactly what you think it will do.
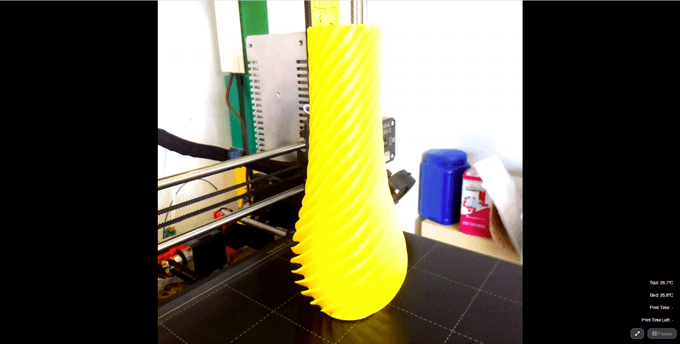
10.CustomBackground
Lastly, who doesn’t want a picture of Captain Picard on the background of their temperature output tab? Drop in any pic, and it’ll show up in the background. Fun!
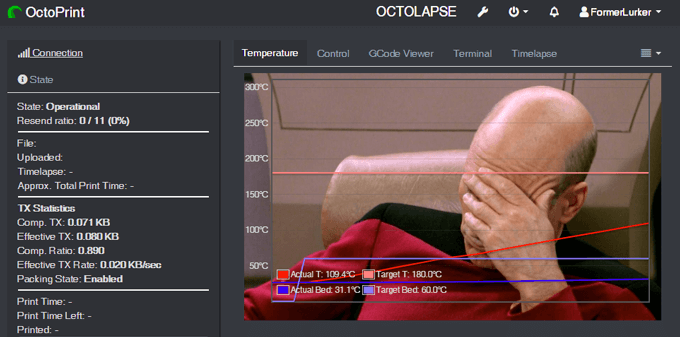
*Full disclosure: The Arc Welder and OctoLapse plugins were created in the attic by my husband, FormerLurker .
- The Best Free AI Courses to Boost Your Skills
- 6 Best Procreate Alternatives for Windows PC
- 5 Best Podcast Apps for Windows
- Best 10 Free PDF Editors for Windows
- 5 Best Audiobook Players for Windows
Maggie Marystone is a freelance technology writer, human rights worker, and storyteller based in Chicago. Read Maggie’s Full Bio
3D printing has become a much more mainstream technology, with printing machines available at just about every price point. Most people who want a 3D printer can probably find a model they can afford. Despite this, 3D printing is still so new that few people know how it works.
This is why now is a good time to answer the question “How does 3D printing work?”. There’s a very good chance you’ll have to use one eventually!

Additive vs Subtractive 3D Printing
There are two broad categories of 3D printing. The 3D printers that you can buy yourself are almost all “additive” machines. In other words, they build 3D objects by adding material (usually in layers) until the object is complete. The 3D printers people think of when they hear “3D printer” is almost always of the additive variety.
Subtractive 3D printing is very different. Here you start with a fixed amount of material and then remove material until only the finished object is left. A sculptor making a statue out of marble is using a subtractive method. Subtractive machines are usually found in large workshops and industrial settings. CNC milling (computer numerical control) systems are probably the best-known example.
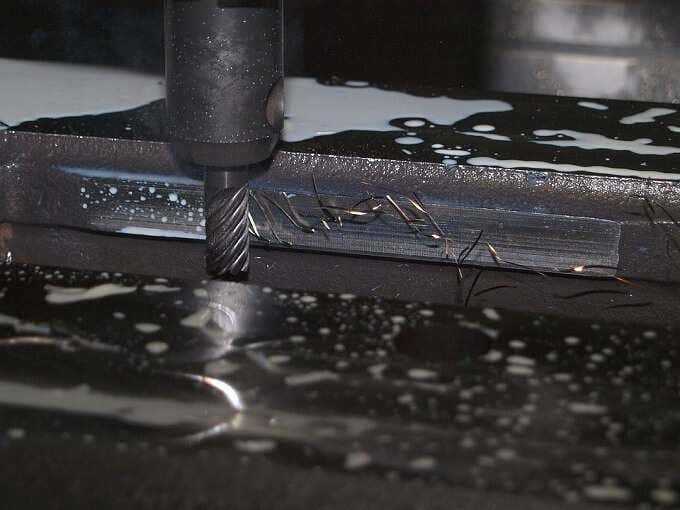

We’ll only be concentrating on additive machines from here on out, since they’re relevant to the average consumer. Just know that subtractive machines belong to the same extended family of 3D printers as the one you might put on a desk.
Fused Deposition Modelling, Stereolithography and Selective Laser Sintering
The three main methods of additive 3D printing are FDM (fused deposition modelling), stereolithography (SLA) and selective laser sintering (SLS).
The da Vinci FDM Printer

FDM is the most common consumer-grade system. With these types of printers a filament of material is passed through a hot print head. The print head is precisely positioned in 3D-space and deposits a layer of material according to exact programmed instructions. There are different approaches to FDM, but we’ll get to that in a moment.
The Nobel SLA Printer
Stereolithography is much less common in consumer systems. These printers use lasers to cure a liquid resin into a solid plastic material. Usually, the object is “pulled” from a vat of resin, forming layer by layer as it rises from the material. In recent years SLA printers have become more compact and affordable. So it’s a real alternative to FDM printers, depending on what type of final model you settle on.
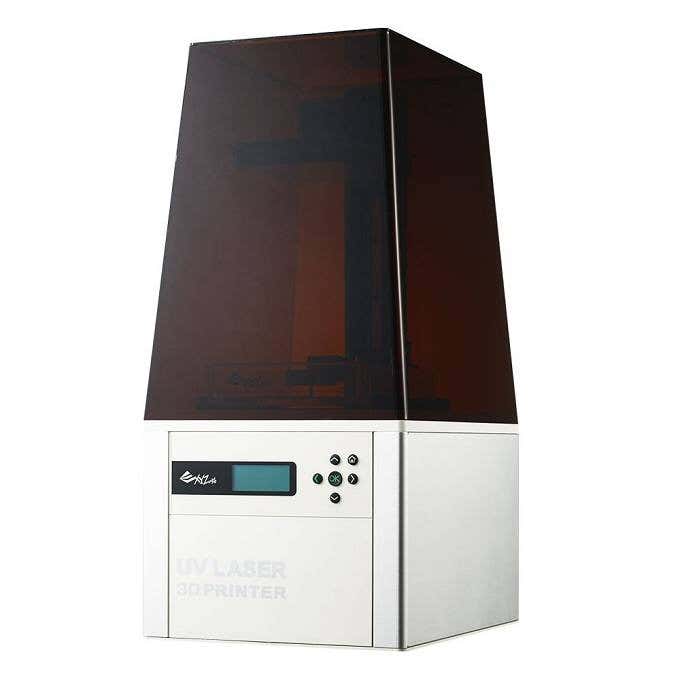

Selective laser sintering (SLS) uses a powerful laser to fuse a polymer powder. The actual powder acts as a support structure for the print, so this type of printing doesn’t need special scaffolding. SLS is not a type of FDM you’ll find on the desktop. It’s still an industrial technology for now.
Cartesian & Delta Robot Printers
A Delta Robot Printer
The most common type of FDM printer is the cartesian 3D printer. The name refers to cartesian coordinates. That’s the XYZ coordinates we all learned in school. The print head can be moved to any XYZ coordinate within the print volume space. The math is simple, the printers are pretty affordable and print quality is precise.
However, depending on how granular the XYZ coordinates are, curved surfaces might not be as smooth as they could be, requiring some manual finishing work.
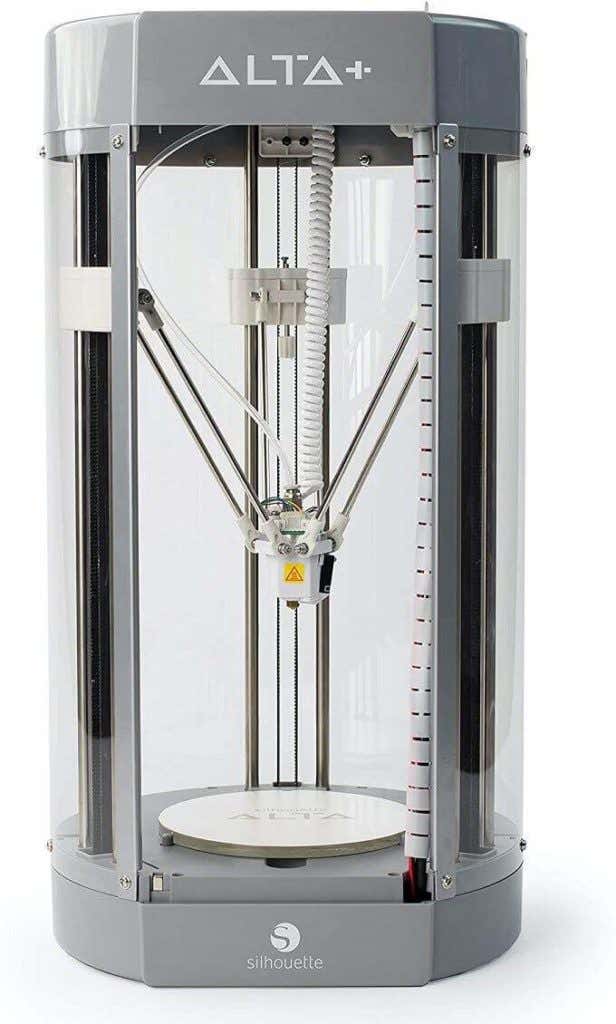

Delta robot printers take a different approach. The print head is mounted to three arms that run on three rails. By varying the height of each arm, the print head can swing. This design allows for the print head to swing in true curves and also allows for tall objects to be printed within the print volume.
Basically, the longer the rails are, the taller the model can be. Rather than XYZ coordinates, delta robot printers use trigonometry to calculate print head position. The end result is that they can’t reach quite the same print resolution as cartesian printers.
To really understand the delta robot concept, you need to see it in action. Have a look at this video by Johann Rocholl and you’ll quickly get the concept.
Notice the articulation on the arms and how freely and smoothly the print head can move.
3D Printer Materials
3D printers use a variety of materials, but there are two plastics that are by far the most common in consumer-grade applications: ABS and PLA.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is exactly the same plastic that LEGO bricks are made of. This plastic is susceptible to warping when cooling down and needs a printer with a heated print bed. It’s quite impact resistant, but not particularly strong. It’s suitable for making prototype parts and even final parts that aren’t load-bearing.

PLA (Polylactic Acid) has a low melting point, doesn’t warp much, is easy to work with and has fewer failed prints. It’s also far too brittle for any practical use, but it is brilliant for creating smooth, detailed models that are only meant to be looked at.
The good news is that most consumer 3D printers will work with both of these inexpensive materials. So you can change them out as your needs require.
Nylon filament is another option and there are even printers that use wood or metal as a material. Next-generation printers can also handle more than one filament at a time, allowing for mixed material or multi-color prints.
The Typical 3D Printing Process
If you’ve never made a 3D print yourself, you’re probably curious about how it actually works from a user perspective. While using a 3D printer isn’t as easy as knocking out 2D prints on a laser or inkjet printer, it’s not nearly as difficult as you might think.
After setting up the printer according to the manual, with calibration and levelling done correctly, you first need a model to print.
You can make your own model, using something like Zbrush or AutoCAD , but most people are likely to download a model from an online site. The first stop should definitely be Thingiverse , which is quite possibly the most famous collection of user-submitted models. However, there are many alternatives.
After getting a model in a compatible format, you’ll open it up in the software that came with your printer. They all look and work differently, but the basic concept is the same. You may also want to first treat a 3D model with Meshmixer , which ensures that a 3D model is solid and suitable for printing.
In the 3D printer software, you’ll pick the size and quality of the model and the software will convert it into “slices” representing each print layer. It will also calculate the “scaffolding” that has to be printed to support the model while it’s being made. This stuff can be broken off when the print is done.
With all that prep work behind you, the print can begin. Depending on the quality settings, you might be in for a long wait! High quality prints vary from a few hours to a few days. Thankfully, some 3D printers let you monitor the progress of your print remotely via an app.
Once the print is done, you’ll remove it from the bed and then break it free of the scaffolding. In many cases you’ll have to finish the model using sandpaper and special cutting tools to remove imperfections. Some people even paint their models! The only real limit is your creativity.
If you’re itching to buy a 3D printer, these are our best picks and if you’re on a budget, these are more pocket friendly options.
- 10 Troubleshooting Tips for 3D Resin Prints Gone Awry
- How to Access and Change Your WiFi Router Settings (2025 Edition)
- HDMI Cable Types and Specifications Explained
- How to Fix the “Error – Printing” Status Error in Windows
- HP Printer Not Printing Black? 10 Fixes to Try
Sydney Butler is a social scientist and technology fanatic who tries to understand how people and technology coexist. He has two decades of experience as a freelance computer technician and more than a decade as a technologies researcher and instructor. Sydney has been a professional technology writer for more than five years and covers topics such as VR, Gaming, Cyber security and Transhumanism. Read Sydney’s Full Bio